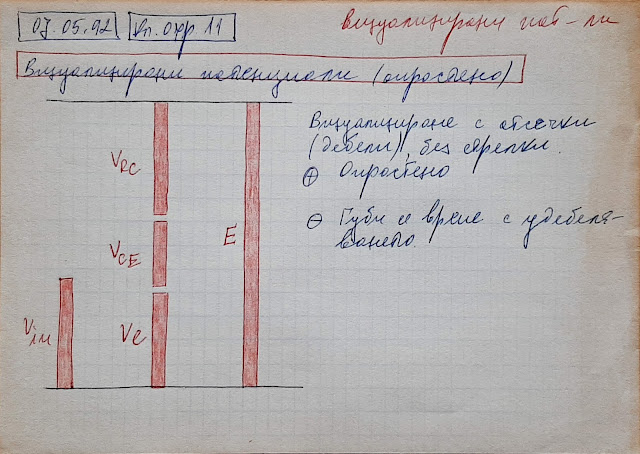
How does a diode maintain a constant voltage?
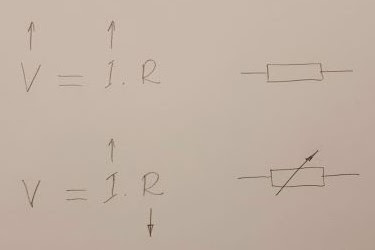
A fundamental property of all types of diodes (silicon, germanium, Schottky, LEDs, Zener ...) is to maintain a relatively constant voltage when the current through them varies. How do they do that? This question can be answered specifically by considering the processes in the semiconductor PN junction. Also, it would be interesting to explain this on a conceptual level by revealing the basic idea. This "philosophical" approach has several advantages: first, it does not require in-depth knowledge of semiconductor devices; second, it would be applicable to all 2-terminal devices that have this property. I will do this using the concept of "dynamic resistance". In the most general sense, a diode behaves like a resistor that interferes with current creating a voltage drop and heat loss. In the initial sloping part of its IV curve, this "resistor" has a relatively constant high resistance. And if it was really a resistor, the curve would continue in the same di